Welcome to InsightFinder AI Observability Docs!
Categories
InsightGateway SDK
A powerful and user-friendly Python SDK for the InsightFinder AI platform. This SDK provides easy-to-use methods for chatting with AI models, evaluating responses, managing sessions, and more.
Installation
Basic Setup
Choose Your Setup Method
Method 1: Use LLM Gateway (Recommended for most users)
- Use when you need high availability and automatic failover
- Best for production applications requiring high uptime
- Ideal for getting started quickly without session management
- Perfect for prototyping and development
- Key: Do NOT provide session_name to activate gateway
Method 2: Specific Session
- Use when you need direct control over a specific model
- Best for research requiring consistent model behavior
- Ideal for testing specific model capabilities
- Perfect for custom or fine-tuned models
- Key: Provide session_name to bypass gateway
Note: The api_key is the InsightFinder account license key.
# Method 1: Use LLM Gateway with fallback models (no session_name required)
# If session_name is not provided, the client will use the LLM Gateway service
# where you can configure Primary LLM, First Backup LLM, and Second Backup LLM
# The system will automatically fallback if the primary model fails
# 1.1: Direct credentials
client = Client(
username=”your_username”,
api_key=”your_api_key” # license key
)
# 1.2: Set environment variables to avoid credentials in code:
# Use environment variables
# export INSIGHTFINDER_USERNAME=”your_username”
# export INSIGHTFINDER_API_KEY=”your_api_key”
client = Client()# Method 2: Specific Session
# 2.1: Direct credentials
client = Client(
session_name=”my-ai-session”,
username=”your_username”,
api_key=”your_api_key”,
enable_chat_evaluation=False # Show evaluation results (default: True)
)# 2.2: Set environment variables to avoid credentials in code:
# Use environment variables
# export INSIGHTFINDER_USERNAME=”your_username”
# export INSIGHTFINDER_API_KEY=”your_api_key”
client = Client(session_name=”my-ai-session”)
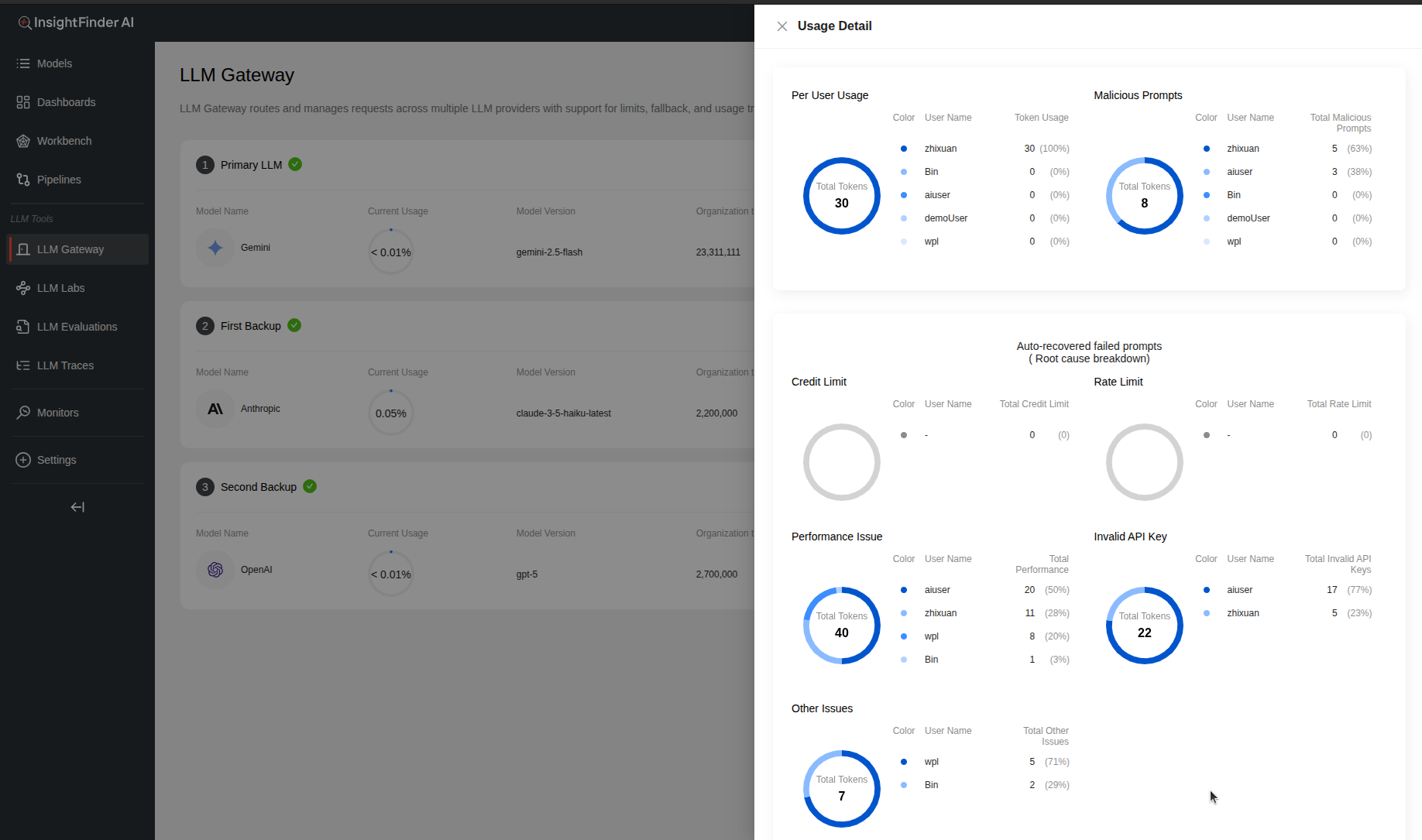
LLM Gateway Service
The LLM Gateway service provides automatic failover capabilities when you don’t specify a session_name. This service allows you to configure multiple models with automatic fallback behavior.
How It Works
When you create a client without a session_name, the system uses the LLM Gateway which includes:
- Primary LLM: Your main model that handles all requests initially
- First Backup LLM: Automatically used if the primary model fails
- Second Backup LLM: Used as the final fallback if both primary and first backup fail
Note: It is mandatory to define a primary model in the InsightFinder AI platform.
Defining first and second backup models is optional, but highly recommended to improve reliability and reduce downtime in case of model failures.
client = Client(
username=”your_username”,
api_key=”your_api_key”
)# All chat operations will use the gateway with automatic fallback
response = client.chat(“Hello world”)
# If primary model fails → tries first backup
# If first backup fails → tries second backup
Benefits
- High Availability: Automatic failover ensures your application keeps working
- No Code Changes: Fallback is transparent to your application
- Centralized Configuration: Manage model preferences in one place
- Cost Optimization: Use cheaper backup models when primary is unavailable
The LLM Gateway SDK automatically generates data such as malicious prompt detections, failed prompt recovery details, and user-level token usage statistics, which are then visible in the InsightFinder AI UI.
Chat Operations
Basic Chat
response = client.chat(“What is artificial intelligence?”)
print(response)# Chat with streaming (shows response as it’s generated)
response = client.chat(“Tell me a story”, stream=True)# Chat without history (independent messages)
response = client.chat(“What’s 2+2?”, chat_history=False)
Chat with Different Sessions
response = client.chat(“Hello”, session_name=”custom-session”)
Evaluation Features
-
Single Evaluation
result = client.evaluate(
prompt=”What’s 2+2?”,
response=”The answer is 4″
)
print(result)
-
Safety Evaluation
result = client.safety_evaluation(“What is your credit card number?”)
print(result) # Shows PII/PHI detection results
-
Batch Evaluation
pairs = [
(“What’s 2+2?”, “4”),
(“Capital of France?”, “Paris”),
(“Tell me a joke”, “Why did the chicken cross the road?”)
]
results = client.batch_evaluate(pairs)
for result in results:
print(result)
-
Batch Safety Evaluation
prompts = [“Hello”, “What’s your SSN?”, “Tell me about AI”]
results = client.batch_safety_evaluation(prompts)
for result in results:
print(result)
Session Management
-
List Sessions
sessions = client.list_sessions()
for session in sessions.sessions:
print(f”Name: {session.name}”)
print(f”Model: {session.model_type}/{session.model_version}”)
print(f”Tokens: {session.token_usage.input_tokens}/{session.token_usage.output_tokens}”)
-
Create New Session
success = client.create_session(
model_name=”my-gpt-session”,
model_type=”OpenAI”,
model_version=”gpt-4o”,
description=”My GPT-4 session”
)
if success:
print(“Session created successfully”)
-
Delete Session
success = client.delete_session(“my-old-session”)
if success:
print(“Session deleted successfully”)
-
List Supported Models
models = client.list_supported_models()
for model in models:
print(model) # Format: “ModelType/ModelVersion”
System Prompt Management
-
Set System Prompt
response = client.set_system_prompt(
“You are a helpful assistant that always responds in JSON format”
)
print(response)# Check if it was applied
if hasattr(response, ‘system_prompt_applied’) and response.system_prompt_applied:
print(“System prompt applied successfully”)
-
Apply System Prompt (Force)
success = client.apply_system_prompt(
“You are a helpful assistant that responds briefly”
)
if success:
print(“System prompt applied”)
-
Clear System Prompt
success = client.clear_system_prompt()
if success:
print(“System prompt cleared”)
Batch Operations
-
Batch Chat
prompts = [“Hello!”, “What’s the weather?”, “Tell me a joke”]
responses = client.batch_chat(prompts, max_workers=3)# Access individual responses
for i, response in enumerate(responses.results):
print(f”Prompt {i+1}: {response.response}”)# Get summary statistics
print(f”Success rate: {responses.success_rate}”)
print(f”Average response time: {responses.average_response_time}”)
Model Comparison
prompts = [
“What is artificial intelligence?”,
“Explain machine learning”,
“Tell me a joke”
]comparison = client.compare_models(
session1_name=”gpt-4-session”,
session2_name=”claude-session”,
prompts=prompts
)# Print side-by-side comparison
comparison.print()# Check which performed better
if comparison.comparison_summary[‘better_performing_model’] != ‘tie’:
print(f”Better model: {comparison.comparison_summary[‘better_performing_model’]}”)
Model Information
Token Usage for Session
usage = client.token_usage(“my-session”)
print(f”Input tokens: {usage.input_tokens}”)
print(f”Output tokens: {usage.output_tokens}”)
Organization Usage Statistics
stats = client.usage_stats()
print(f”Total input tokens: {stats.total_input_tokens}”)
print(f”Total output tokens: {stats.total_output_tokens}”)
print(f”Token limit: {stats.total_token_limit}”)
Cache Management
Clear Caches
client.clear_project_name_cache()# Clear model info cache
client.clear_model_info_cache()# View cached data
project_names = client.get_cached_project_names()
model_info = client.get_cached_model_info()
Working with Response Objects
ChatResponse Object
print(f”Response: {response.response}”)
print(f”Prompt: {response.prompt}”)
print(f”Model: {response.model}”)
print(f”Model Version: {response.model_version}”)
print(f”Trace ID: {response.trace_id}”)
print(f”Session: {response.session_name}”)
print(f”Tokens: {response.prompt_token}/{response.response_token}”)# Check if evaluations are available
if response.evaluations:
print(“Evaluation results available”)# Pretty print (formatted output)
response.print()
EvaluationResult Object
print(f”Trace ID: {result.trace_id}”)
print(f”Prompt: {result.prompt}”)
print(f”Response: {result.response}”)
print(f”Model: {result.model}/{result.model_version}”)# Pretty print evaluation results
result.print()
Advanced Configuration
LLM Gateway vs Session-Based Usage
client = Client(
username=”your_username”,
api_key=”your_api_key”
)
# Automatically uses Primary → First Backup → Second Backup LLMs# Option 2: Use specific session (direct model access, no fallback)
client = Client(
session_name=”my-gpt-session”,
username=”your_username”,
api_key=”your_api_key”
)
# Uses only the model configured for “my-gpt-session”
Custom API URL
client = Client(
session_name=”my-session”,
url=”https://custom-api.example.com”,
username=”user”,
api_key=”key”
)
Disable Evaluations
client = Client(
session_name=”my-session”,
enable_chat_evaluation=False
)# Or disable for specific chat
response = client.chat(“Hello”, enable_evaluation=False)
Custom Session Names in Operations
client.chat(“Hello”, session_name=”session-1″)
client.evaluate(“Test”, “Response”, session_name=”session-2″)
client.set_system_prompt(“System prompt”, session_name=”session-3″)
client.clear_context(session_name=”session-4″)
Error Handling
response = client.chat(“Hello”)
print(response)
except ValueError as e:
print(f”API Error: {e}”)
except Exception as e:
print(f”Unexpected error: {e}”)
Environment Variables
Set these environment variables to avoid passing credentials in code:
export INSIGHTFINDER_API_KEY=”your_api_key”
From the Blog
Explore InsightFinder AI